What Is Oocyte Freezing?
Oocyte Freezing also known as egg freezing, is a process where a woman’s eggs (oocytes) are retrieved, frozen, and stored for future use. This technique helps women preserve their fertility and increase their chances of conceiving later in life. The frozen eggs can be thawed, fertilized with sperm, and implanted through in vitro fertilization (IVF) when the woman is ready for pregnancy.
Why Do Women Choose Oocyte Freezing?
Women opt for oocyte freezing for several reasons, including:
Delaying Motherhood: Career, education, or personal reasons may delay pregnancy.
Medical Conditions: Cancer treatments, surgeries, or autoimmune diseases that can affect fertility.
Premature Ovarian Failure: Family history of early menopause.
Gender-Affirming Procedures: For transgender individuals before hormone therapy or surgery.
Fertility Preservation Before IVF: Some women freeze eggs before undergoing IVF for better success rates.
Step-by-Step Procedure of Oocyte Freezing
1. Ovarian Stimulation
The patient takes hormone injections for 10-14 days to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
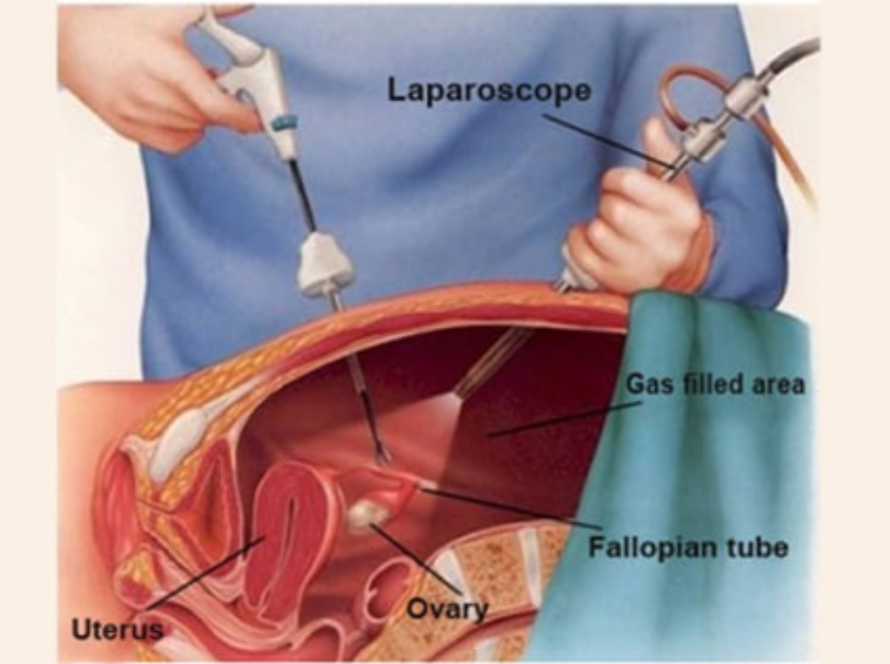
2. Egg Retrieval (Oocyte Aspiration)
Once the follicles mature, a minor surgical procedure is performed under sedation to collect the eggs from the ovaries.
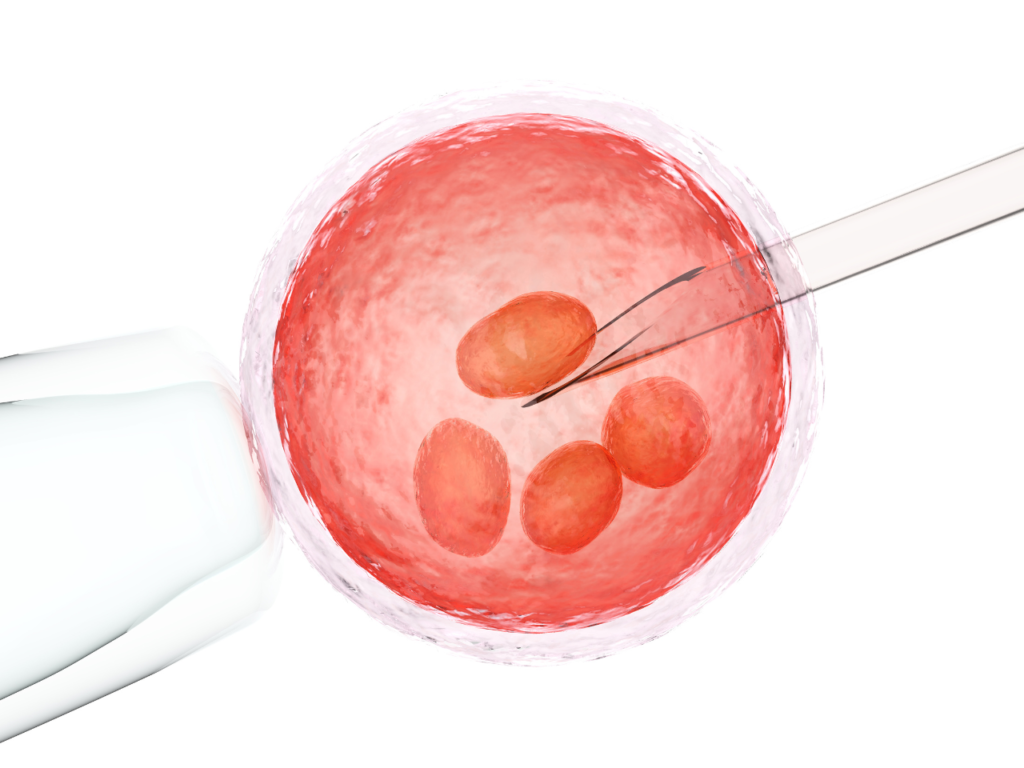
3. Egg Freezing (Cryopreservation)
The retrieved eggs are immediately frozen using vitrification, a rapid freezing process that prevents ice crystal formation.
4. Storage in Cryobank
The frozen eggs are stored in liquid nitrogen at -196°C until they are needed for fertilization.
5. Future Fertilization and IVF
When the woman decides to conceive, the eggs are thawed, fertilized with sperm in a lab, and transferred into the uterus via IVF.
Benefits of Oocyte Freezing
Preserves Fertility: Allows women to have biological children later in life.
Higher Pregnancy Success Rates: Freezing eggs at a younger age increases the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Provides Reproductive Freedom: Women can plan their families without worrying about age-related fertility decline.
Medical Security: Helps women undergoing medical treatments that may impact fertility.
Better IVF Outcomes: Freezing eggs early may result in healthier embryos in the future.
Who Should Consider Oocyte Freezing?
Women in their 20s or early 30s who want to delay pregnancy.
Women with a family history of early menopause.
Cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiation.
Women with endometriosis or other fertility-impacting conditions.
Individuals planning gender-affirming treatments.
Success Rates and Limitations
The age of egg freezing is a key factor in success rates.
Eggs frozen before age 35 have a higher chance of leading to pregnancy.
Not all eggs survive thawing, fertilization, and implantation.
Multiple eggs may be required to achieve a successful pregnancy.
FAQs
Eggs can be stored indefinitely, with successful pregnancies reported from eggs frozen for over 10 years.
The best time is before age 35, as egg quality declines with age.
The procedure is performed under sedation, so there is minimal discomfort.
Doctors recommend freezing at least 10-15 eggs for a good success rate.
While it increases the chances of pregnancy, success is not 100% and depends on factors like age and overall reproductive health.
Conclusion:
Oocyte freezing is a powerful tool for women who want to take control of their fertility. With advancements in reproductive medicine, this technique provides hope for those looking to delay motherhood or preserve their fertility due to medical reasons. If you are considering egg freezing, consult a fertility specialist to understand the best options for you.